JUnit5 : Annotation, Assertion
2020. 12. 18. 23:44
728x90
JUnit5 세부모듈
- JUnit Platform : 테스트를 실행해주는 런처제공, TestEngine API 제공
- JUnit Jupiter : TestEngineAPI 구현체로 JUnit5를 제공
- JUnit Vintage : JUnit4와 JUnit3을 지원하는 TestEngine구현체
Annotation
| @Test | 테스트임을 나타낸다. |
|
@BeforeAll |
현재 클래스에서 모든 메서드 전에 실행됨. 메소드는 static 이어야 한다. |
| @AfterAll | 현재 클래스에서 모든 메서드 후에 실행됨. 메소드는 static 이어야 한다. |
| @BeforeEach | 각각의 테스트 메서드 전에 실행됨. |
| @AftetEach | 각각의 테스트 메서드 후에 실행됨. |
| @Disabled | 테스트 클래스나 메서드를 비활성화 할때 사용. |
| @DisplayName | 테스트 클래스 또는 테스트 메서드의 이름을 정의할 때 사용. |
//@BeforeAll, @AfterAll, @BeforeEach, @AftetEach
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class StudyTest {
@Test
void create() {
Study study = new Study();
assertNotNull(study);
System.out.println("creat");
}
@Test
void create1() {
System.out.println("create1");
}
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("before all");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("after all");
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("before each");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("after each");
}
}
// 결과
before all
before each
creat
after each
before each
create1
after each
after all
//@DisplayNameGeneration, @DisplayName
@DisplayNameGeneration(DisplayNameGenerator.ReplaceUnderscores.class)
class StudyTest {
@Test
void create_new_study() {
Study study = new Study();
assertNotNull(study);
System.out.println("creat");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("스터디 만들기!")
void create1() {
System.out.println("create1");
}
}
// 실행
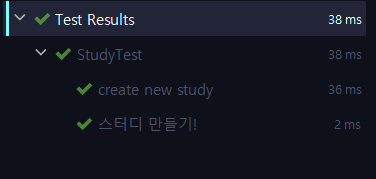
Assertion
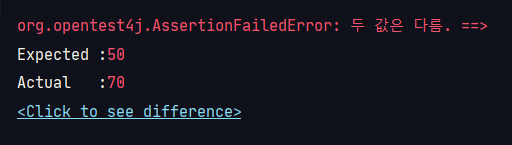
assertEquals
: 두 값이 같은지 확인할 때 사용
@Test
public void assert_equals() {
int a = 50;
int b = 70;
assertEquals(a,b, ()->"두 값은 다름.");
}
//결과
assertArrayEquals
: 두 배열의 값이 같은지 확인할 때 사용.
@Test
public void assert_array_equals() {
String[] array1 = {"asd", "qwe", "ert", "xcv", "fgd"};
String[] array2 = {"aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd", "eee"};
assertArrayEquals(array1, array2, "두 배열의 값이 다르다.");
}
// 결과

assertNotEquals
: 두 값이 같지 않은지 확인할 때 사용.
@Test
public void assert_not_equals() {
int a = 100;
assertNotEquals(100, a, "값이 같습니다.");
}
// 결과

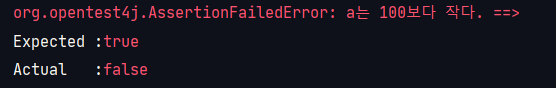
assertTrue
: true인지 확인할 때 사용.
@Test
public void assert_true() {
int a = 5;
assertTrue(a>100, "a는 100보다 작다.");
}
// 결과
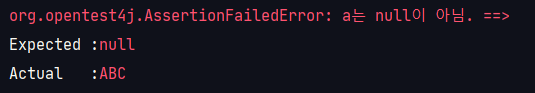
assertNull
: Null인지 확인할 때 사용, <=> assertNotNull
@Test
public void assert_null() {
String str = "ABC";
assertNull(str, "a는 null이 아님.");
}
// 결과
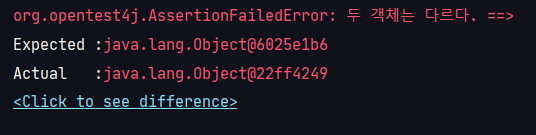
assertSame
: 두 객체가 같은 주소값을 가지는지 확인할 때 사용. <=> assertNotSame
@Test
public void assert_same() {
Object obj = new Object();
Object obj2 = new Object();
assertSame(obj,obj2, "두 객체는 다르다.");
}
// 결과
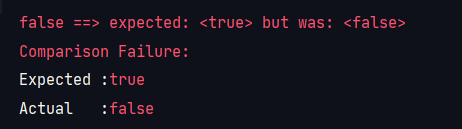
assertAll
: 한번에 여러 테스트를 할 때 사용, 모두 성공해야 성공.
@Test
public void assert_all() {
int a = 0;
assertAll(
()-> assertEquals(2, 2, "두 값은 다르다"),
()-> assertTrue( 4<2, "false"),
()-> assertNotNull( a , "null")
);
}
// 결과
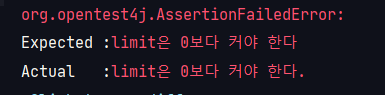
assertTrows
: 예외 테스트를 할 때 사용.
@Test
public void assert_throws() {
IllegalArgumentException exception = assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> new Study(-10));
assertEquals("limit은 0보다 커야 한다", exception.getMessage());
}
// 결과
assertTimeout
: timeout 테스트를 할 때 사용. timeout에 걸려도 멈추지 않고 실행된다.
@Test
public void assert_timeout() {
assertTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(100), () ->{
new Study(10);
Thread.sleep(1000);
});
}
// 결과

assertTimeoutPreemptively
: timeout에 걸리면 종료된다.
@Test
public void assert_timeout_preemptively() {
assertTimeoutPreemptively(Duration.ofMillis(100), () ->{
new Study(10);
Thread.sleep(1000);
});
}
// 결과

728x90








